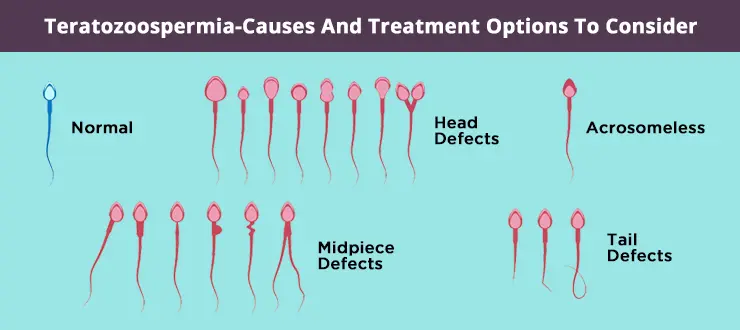
Teratozoospermia is a medical condition impacting male fertility, characterized by a high proportion of abnormally shaped sperm within a semen sample. While healthy sperm have an oval head and long tail, sperm affected by teratozoospermia often display irregular forms, which can compromise their ability to fertilize an egg. This blog will explore the causes, implications, and current treatment options available for teratozoospermia, offering hope and guidance to those facing related fertility challenges.
Teratozoospermia, also called teratospermia, stems from the Greek word “terato,” meaning “monster” or “malformed.” This generally takes place among men and becomes a major cause of infertility. Men with this condition typically receive the diagnosis following a semen analysis when less than 4% of sperm have normal morphology per WHO guidelines. The most important thing to take into consideration is that teratozoospermia doesn’t always mean that natural conception is impossible.
If we talk about the display of an ordinary sperm, it is comprised of some parts like tail, neck,
head, and mid-piece. The width is counted as 2-3 micrometers, whereas it has been supposed to be around 3-5 micrometers in length. The shape of its head is oval, which is covered by a
structure known as the acrosome.
It’s essential to understand that teratozoospermia is not a disease itself but a symptom or manifestation of underlying issues. According to some research, some activities can affect the health of sperm, like chemotherapy and radiation therapy, which are given to a patient suffering from cancer. Along with that, there has been an identification of some drugs that can interact with hormones developed in the body like follicle-stimulating hormone, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, and testosterone hormone, to cause changes in the production of sperm and resulting in incomplete maturation. Several factors can contribute to the development of abnormal sperm morphology:
Teratozoospermia has been said as one of the causes behind infertility in men due to the fact that most abnormal spermatozoa don’t get able to penetrate the egg. The quality of sperm can be affected by some factors like problems in the testicles, vasectomies, fevers, diabetes mellitus, smoking, and usage of alcohol, cocaine, and marijuana, poor diet, varicocele, and inappropriate habits that elevate the temperature in the testicles.
Three different types of teratozoospermia are there to explored like mild teratozoospermia,
moderate teratozoospermia, and severe teratozoospermia. In mild teratozoospermia, the usual
sperm morphology value ranges from 10 to 14%. Moderate teratozoospermia holds a value
between 5-9%, whereas severe teratozoospermia contains a normal sperm morphology value of
less than 5%. The typical shape of the sperm allows it to swim across the female genital tract to obtain the ovum and fertilize it. If a defect is found in the tail, it may hamper sperm motility. Even if an abnormality is identified in the sperm head, it may lead to unsuccessful penetration of the ovum by the sperm.
One more thing related to teratozoospermia is whether it causes miscarriage. To identify this
thing, there will be a requirement to know that since the mother carries the baby in her womb, causes for miscarriages are typically credited to maternal factors. The chances of paternal
factors, particularly the sperm based factors, have been overlooked in previous times. It is
suggested that those who faced miscarriage, especially recurrent pregnancy losses, must focus on testing for both maternal and paternal factors.
Most men with teratozoospermia do not experience physical symptoms. Moreover they don’t even recognise it until and unless they are into the fertility assurance. The condition commonly comes to light during fertility testing, especially when couples encounter challenges in trying to conceive. Diagnosis involves semen analysis, where the percentage of normally shaped sperm is measured. A score below the standard threshold raises the flag for teratozoospermia.
When teratozoospermia is identified by a person, the focus must be on its treatment.
Treatment for teratozoospermia depends largely on its causes and the severity of the condition. The aim is to improve sperm morphology, thereby increasing the chances of conception. Modern medicine offers a spectrum of solutions, which can be categorized as follows:
Making healthy lifestyle choices is often the foundational and most accessible approach, particularly in mild cases:
Research suggests that supplementing with antioxidants such as vitamin E, vitamin C, coenzyme Q10, L-carnitine, and omega-3 fatty acids may help improve sperm morphology and motility.
Depending on the underlying cause, specific medical interventions may be necessary:
When conventional treatments fail, ART offers hope:
Emerging evidence has highlighted the importance of antioxidants, genetic analysis, and advanced sperm selection techniques in the management of teratozoospermia. Plant-based diets are also being investigated for their potential in preventing and improving sperm morphology. Despite these advancements, high-quality evidence for standard treatment protocols remains limited, and further research is advocated to strengthen recommendations.
A diagnosis of teratozoospermia can be distressing, but it does not spell the end of fatherhood ambitions. Many men with this condition ultimately achieve successful pregnancies with lifestyle changes, targeted treatments, or assisted reproductive technologies. Early and open communication with healthcare providers, ongoing lifestyle adjustments, and consideration of all available treatment options are key steps in overcoming teratozoospermia-related fertility challenges.
Teratozoospermia is a multifaceted condition influenced by genetic, environmental, medical, and lifestyle factors. With the right interventions—ranging from lifestyle improvements and nutritional support to advanced medical and reproductive technologies—many affected men can significantly boost their fertility prospects. If you or your partner experiences challenges with conception, consult a fertility specialist at Aveya IVF Centre for customized advice and support. With awareness and proactive management, teratozoospermia can be mitigated, and family-building goals can remain within reach.
Q1. What is Teratozoospermia?
Teratozoospermia is a condition in which a man’s sperm have abnormal shapes (morphology). Since the shape of sperm affects its ability to swim and fertilize an egg, this condition can contribute to male infertility.
Q2. What causes Teratozoospermia?
The exact cause may vary, but some common factors include:
Q3. How is Teratozoospermia diagnosed?
It is usually diagnosed through a semen analysis, which examines sperm count, motility, and morphology under a microscope.
Q4. Can men with Teratozoospermia still father a child naturally?
It depends on the severity of abnormal sperm morphology. In mild cases, natural conception is possible, but in severe cases, fertility treatments may be needed.
Q5. What lifestyle changes can help improve sperm morphology?
Q6. What medical treatments are available for Teratozoospermia?
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
Q7. What fertility treatments can help if natural conception is difficult?
Q8. Is Teratozoospermia permanent?
Not always. With lifestyle improvements and medical treatment, sperm morphology can sometimes improve. However, in some cases, advanced fertility techniques may still be required.
Q9. Can Teratozoospermia be prevented?
While genetic causes cannot be prevented, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, avoiding toxins, and treating medical conditions early can reduce the risk of developing abnormal sperm morphology.
Q10. When should I see a fertility specialist?
If you and your partner have been trying to conceive for over a year (or six months if the female partner is over 35), and especially if semen analysis shows Teratozoospermia, consulting a fertility specialist is highly recommended.